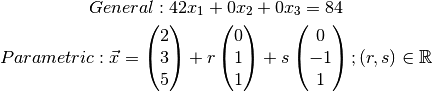4. Examples¶
4.1. Point on Line¶
Given point 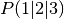 and line
and line
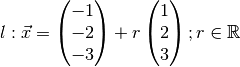 , is P on l?
, is P on l?
from sgl import *
p = Point(1, 2, 3)
l = Line(Point(-1, -2, -3), Vector(1, 2, 3))
print(p in l)
Output:
True
4.2. Line comparison¶
Are the lines
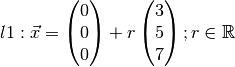 and
and
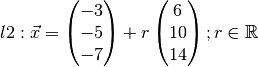 the same?
the same?
from sgl import *
l1 = Line(Point(0, 0, 0), Vector(3, 5, 7))
l2 = Line(Point(-3, -5, -7), Vector(6, 10, 14))
print(l1 == l2)
Output:
True
4.3. Pyramid¶
Given Points 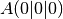 ,
, 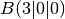 ,
, 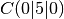 and
and 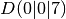 . Compute the area of the Triangle
. Compute the area of the Triangle 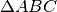 and the volume of the pyramid ABCD.
and the volume of the pyramid ABCD.
from sgl import *
A = Point(0, 0, 0)
B = Point(3, 0, 0)
C = Point(0, 5, 0)
D = Point(0, 0, 7)
# This could be simplified if we account for the fact that this is a
# right-angled triangle, but we're using the generic way here
base = distance(A, B)
baseline = Line(A, B)
baseheight = distance(baseline, C)
area = 0.5 * base * baseheight
print("Area: %f" % area)
# Again we could simplify here, but we're using the generic way
baseplane = Plane(A, B, C)
height = distance(baseplane, D)
volume = 1.0 / 3 * area * height
print("Volume: %f" % volume)
Output:
Area: 7.500000
Volume: 17.500000
4.4. Different representations¶
Give the general form and the parametric form of the plane given by
![P: \left[\vec{x} - \begin{pmatrix}2\\3\\5\end{pmatrix}\right]\begin{pmatrix}42\\0\\0\end{pmatrix} = 0](_images/math/6d676c6ad6399b849c52657a511c7f0d7e44f94e.png)
from sgl import *
plane = Plane(Point(2, 3, 5), Vector(42, 0, 0))
print("General: %ix1 + %ix2 + %ix3 = %i" % plane.general_form())
print("Parametric: x = %s + r * %s + s * %s ; r,s e R" % plane.parametric())
Output:
General: 42x1 + 0x2 + 0x3 = 84
Parametric: x = Vector(2, 3, 5) + r * Vector(0.0, 1.0, 1.0) + s * Vector(0.0, -1.0, 1.0) ; r,s e R
More mathy: